"Guardians of Power: How MCBs Provide Crucial Protection to Electrical Circuits”
- Sep 21, 2023
- 3 min read
Updated: Oct 26, 2023
Key Summary
Maintaining the safety and reliability of electrical systems is crucial due to the potential for electrical fires, equipment damage, and safety hazards.
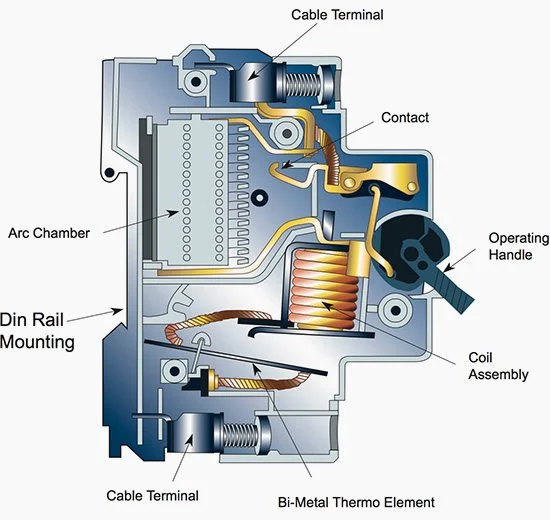
Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) act as silent guardians for electrical circuits, protecting them from overcurrent and short circuits.
MCBs protect circuits from overcurrent, which can lead to overheating, wire insulation damage, and fires.
Proper selection of MCBs involves matching their current rating to the circuit's expected maximum load to ensure both protection and normal operation.
MCBs and MCCBs serve similar functions but differ in size, current handling capacity, trip characteristics, and applications.
Electricity is the lifeline of our modern homes, businesses, and industries. It powers our lights, appliances, equipment, and a vast number of other things that we rely on every day. However, with tremendous power comes great responsibility, and it is critical to ensure the safety and reliability of electrical systems. Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) serve as the silent guardians of our electrical circuits in this situation.
Imagine a world without MCBs, where electrical circuits are exposed to the constant threat of overcurrent and short circuits. It's a recipe for disaster, with the potential for electrical fires, equipment damage, and safety hazards. MCBs are the solution to this problem, serving as the first line of defense against electrical faults.
At the heart of ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical circuits is the commitment of switchboard manufacturers. Kennek Electricals prioritizes safety above all else. We understand that the backbone of any reliable electrical system is the switchboard, and this is where the magic happens. Kennek Electricals takes great pride in designing and manufacturing switchboards that meet the highest safety standards.
The Role of MCBs in Circuit Protection
One of the primary functions of MCBs is to protect circuits from overcurrent. Overcurrent occurs when the current flowing through a circuit exceeds its designed capacity. This can happen due to various reasons, such as a malfunctioning appliance, a wiring fault, or simply plugging in too many devices. Without MCBs, overcurrent could lead to overheating of wires, causing insulation to melt and potentially igniting fires. MCBs monitor the current flow and, when it exceeds a safe limit, they act swiftly by tripping the circuit, and cutting off the power supply to prevent further damage.
Short circuits are another menace that MCBs effectively combat. A short circuit occurs when there's a direct, low-resistance path between the live and neutral conductors, resulting in an exceptionally high current flow. This can happen due to damaged wires, faulty connections, or equipment failures. Without MCBs, a short circuit could cause immediate and severe damage to the electrical system. MCBs, with their rapid response, quickly interrupt the flow of current in such cases, minimizing damage and preventing dangerous situations.
One of the essential aspects of MCBs is their current rating. Each MCB is designed to handle a specific amount of current. When selecting MCBs for circuits, it's crucial to match the MCB's rating to the circuit's expected maximum load. This ensures that the MCB will trip when necessary to protect the circuit but won't trip unnecessarily during normal operation.
“Tripping characteristics describe the operational and tripping behavior of miniature circuit breakers in the event of an overload or short circuit. The tripping curves of the electromagnetic release and the thermal bi-metal release result in an overall tripping curve for overload protection”.(electrical terminology. 2020, December 23). MCBs come with different tripping characteristics, such as B, C, and D curves. These curves determine how quickly the MCB will trip in response to overcurrent. For instance, circuits with motors or inductive loads may require MCBs with higher tripping characteristics (C or D) to handle brief overcurrent during startup without tripping.
MCB vs MCCB

MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers) and MCCBs (Molded Case Circuit Breakers) are both essential electrical devices used to protect circuits from overcurrent and short circuits, but they differ significantly in their size, current handling capacity, trip characteristics, and applications. MCBs are smaller, suited for lower current ratings, and typically used in residential and light commercial settings for individual circuit protection, while MCCBs are larger, adjustable in terms of trip characteristics, and primarily employed in industrial and commercial environments to safeguard larger electrical loads and equipment. MCCBs offer better short-circuit protection and can handle higher fault currents, making them the choice for heavy-duty applications, while MCBs are cost-effective and ideal for smaller-scale electrical systems.
In conclusion, MCBs stand as vigilant protectors. They monitor the flow of current, detect abnormalities, and act swiftly to safeguard circuits and the safety of occupants. Without MCBs, our electrical systems would be vulnerable to overcurrent and short circuits, with dire consequences. Our Kennek Electricals prioritize safety, You can trust that the MCBs included in our switchboards are the epitome of protection and reliability, delivering peace of mind to clients and ensuring a brighter, safer future.
.png)